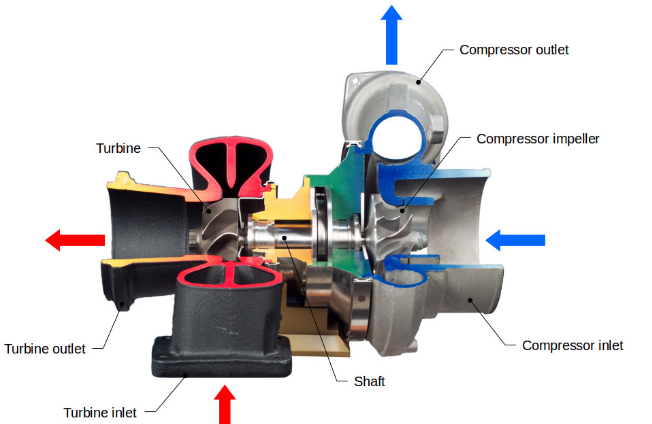
The exhaust gas turbocharger consists of two parts: the exhaust gas turbine and the compressor. Generally, the exhaust gas turbine is on the right side and the compressor is on the left side. They are coaxial. The turbine casing is made of heat-resistant alloy cast iron. The air inlet end is connected to the cylinder exhaust pipe, and the air outlet end is connected to the diesel engine exhaust port. The air inlet end of the compressor is connected to the air filter of the diesel engine air inlet, and the air outlet end is connected to the cylinder air inlet pipe.
1. Exhaust gas turbine
The exhaust gas turbine usually consists of a turbine housing, a nozzle ring and a working impeller. The nozzle ring consists of the nozzle inner ring, outer ring and nozzle blades. The channel formed by the nozzle blades shrinks from the inlet to the outlet. The working impeller is composed of a turntable and an impeller, and working blades are fixed on the outer edge of the turntable. A nozzle ring and the adjacent working impeller form a “stage”. A turbine with only one stage is called a single-stage turbine. Most superchargers use single-stage turbines.
The working principle of the exhaust gas turbine is as follows: When the diesel engine is working, the exhaust gas passes through the exhaust pipe and flows into the nozzle ring at a certain pressure and temperature. Since the channel area of the nozzle ring gradually decreases, the flow rate of the exhaust gas in the nozzle ring increases (although its pressure and temperature decrease). The high-speed exhaust gas coming out of the nozzle enters the flow channel in the impeller blades, and the airflow is forced to turn. Due to the centrifugal force, the airflow presses toward the concave surface of the blade and attempts to leave the blade, causing a pressure difference between the concave and convex surfaces of the blade. The resultant force of the pressure difference acting on all blades produces an impact torque on the rotating shaft, causing the impeller to rotate in the direction of the torque, and then The exhaust gas flowing out from the impeller is discharged from the exhaust port through the center of the turbine.
2. Compressor
The compressor is mainly composed of the air inlet, working impeller, diffuser and turbine housing. The compressor is coaxial with the exhaust gas turbine and is driven by the exhaust gas turbine to rotate the working turbine at high speed. The working turbine is the main component of the compressor. It usually consists of a forward-curved wind guide wheel and a semi-open working wheel. The two parts are respectively installed on the rotating shaft. Straight blades are arranged radially on the working wheel, and an expanded airflow channel is formed between each blade. Due to the rotation of the working wheel, the intake air is compressed due to centrifugal force and is thrown to the outer edge of the working wheel, causing the pressure, temperature and speed of the air to increase. When the air flows through the diffuser, the kinetic energy of the air is converted into pressure energy due to the diffusion effect. In the exhaust turbine housing, the kinetic energy of the air is gradually converted into pressure energy. In this way, the intake air density of the diesel engine is significantly improved through the compressor.
Post time: May-24-2024